2
Andrew Cote (@Andercot)
nitter.netNational Lab (LBNL) results support LK-99 as a room-temperature ambient-pressure superconductor.
Simulations published 1 hour ago on arxiv support LK-99 as the holy grail of modern material science and applied physics.
(https://arxiv.org/abs/2307.16892)
Here's the plain-english explanation:
- The simulations modeled what the original Korean authors proposed was happening to their material - where copper atoms were percolating into a crystal structure and replacing lead atoms, causing the crystal to strain slightly and contract by 0.5%. This unique structure was proposed to allow this amazing property.
- @sineatrix from Lawrence Berkeley National Lab simulated this using heavy-duty compute power from the Department of Energy, and looked to see what would happen to the 'electronic structure' of this material, meaning, what are the available conduction pathways in the material.
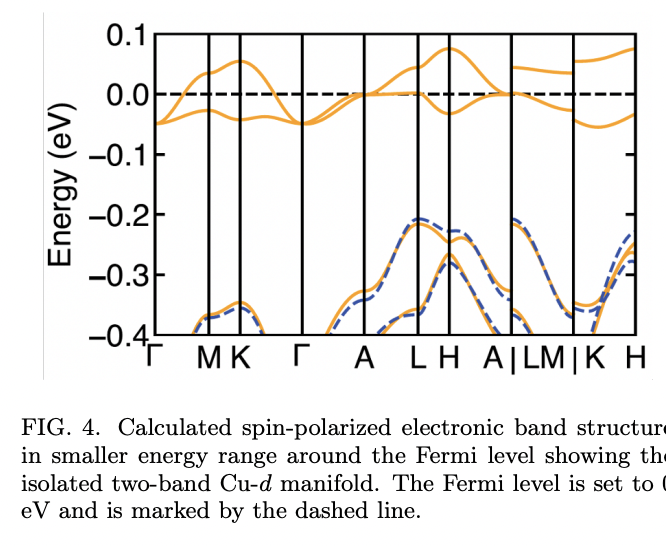
- It turns out that there are conduction pathways for electrons that are in just the right conditions and places that would enable them to 'superconduct'. More specifically, they were close to the 'Fermi Surface' which is like the sea-level of electrical energy, as in '0 ft above sea-level.' It's believed currently that the more conduction pathways close to the Fermi surface, the higher the temperature you can superconduct at (An analogy might be how its easier for planes to fly close to the surface of the ocean due to the 'ground effect' that gives them more lift.)
This plot in particular shows the 'bands', or electron pathways, crossing above and below the Fermi surface.
- Lastly, these interesting conduction pathways only form when the copper atom percolates into the less likely location in the crystal lattice, or the 'higher energy' binding site. This means the material would be difficult to synthesize since only a small fraction of crystal gets its copper in just the right location.
This is insanely bullish for humanity.
You must log in or # to comment.