2021: Flooding
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/2021_European_floods
German minister-president Malu Dreyer of the Rhineland-Palatinate state called the floods “devastating”. In addition to the confirmed fatalities, the flooding led to widespread power outages, forced evacuations and damage to infrastructure and agriculture in the affected areas. The damage to infrastructure was especially severe in Belgium and Germany.
2022: Drought
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/2022_European_drought
Germany
As of August 2022, the River Rhine’s water level had fallen so much that shipping was affected.[22][23] The water level in Emmerich sunk to -3 cm, being 10 cm lower than the previous record from 2018. The normal water level is 239 cm.[24][25] Due to the low water levels, the cost of transporting goods multiplied because ships were only able to load 25-35% of their usual freight.[26]
On 24 August, 54% of the German area was affected by an extraordinary drought. Further 24.6% by an extreme and further 12.2% by a severe drought.[27]
Many districts and states banned water extraction from creeks, rivers and lakes, the watering of lawns, filling of pools or cleaning cars.[27][28]
2024: Flooding
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/2024_European_floods
Germany
Main article: 2024 Germany floods
Flooding in Germany caused at least nine deaths, insured property damage of €2.2 billion, and over 3,000 displaced individuals.[35][36][37][38][39]
In May 2024, over 100 liters of rain per square meter came down in less than 24 hours over Saarland. A woman in Saarbrücken was injured during an evacuation and later died, while a Red Cross worker died following a rescue operation from heart failure.[40]
In June 2024, significant flooding struck Southern Germany, striking the most in Baden-Württemberg and Bavaria. Dozens of villages had to be evacuated across Baden-Württemberg and Bavaria due to the straining and failure of several dams and dykes caused by the persistent heavy rainfall.[41] Among the rivers whose water levels significantly rose include the Danube, the Isar, the Zusam, the Weilach, the Ilm, the Paar, the Schmutter,[42] the Roth, and the Leibi.[43] Many places had more rainfall in 24 hours than their whole monthly average, and in many areas, the water reached levels that were present only “once in a century” according to the Bavarian Flood Information Service.[44]
2025, present-day: Drought
Not enough rain: How can Germany cope with drought?
This spring was one of the driest on record in Germany. Agriculture, groundwater, and even retail prices are suffering. Plants and ecosystems are already in drought stress. What can be done?
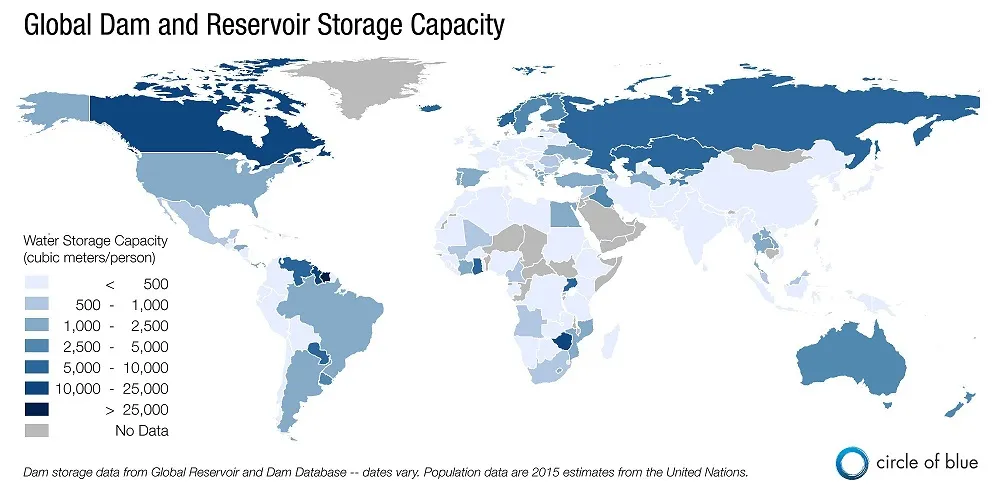
I’m thinking more reservoirs.
EDIT:
https://lemmy.today/pictrs/image/18df5f3f-1a6d-4223-80c0-ae7df3621cb1.webp